Table of content
What is Seed Funding?
Seed funding is the initial capital raised by a startup to develop its business idea before generating significant revenue. The term “seed” represents the early stage of business growth, where capital acts as a foundation for expansion. Seed funding provides startups with the resources they need to validate their concept and build momentum.
Key uses of seed funding include:
- Product development and MVP creation
- Market research and customer validation
- Hiring early team members
- Building initial traction and user base
- Establishing business operations
The name comes from the idea that this early capital is the “seed” from which a business can grow into a larger company. Seed funding is typically the first significant external investment a startup receives.

UK Seed Funding Market Statistics 2026
Understanding the current market landscape is crucial for UK founders seeking seed funding. The UK seed funding market has shown strong growth in recent years.
1. Market Size and Growth
Total UK seed funding in 2024: approximately £2.04 billion, a 24% increase from £1.64 billion in 2023
2. Industry Breakdown
Based on 2023-2024 venture investment trends in the UK, seed funding is being directed across multiple sectors:
- FinTech: regained top spot in 2024 after reclaiming dominance
- CleanTech/ClimateTech: fastest growing among funded sectors, accounting for 29% of VC investment in 2023
3. Geographic Distribution
From Beauhurst’s H1 2024 data on seed funding distribution:
- London: 61.8% of equity funding, and 47.2% of deals
- Scotland: 10.2% of deals
- North West (e.g., Manchester/Liverpool): 10.9% of funding

UK Seed Funding / Early-Stage Investment (2025 Trends)
In the first three quarters of 2025, seed-stage funding in the UK reached about $1.6 billion, up approximately 31% compared to the same period in 2024. This reflects continued investor interest in early-stage deals despite broader market shifts.
Q1 2025 London data shows that seed-stage companies secured £520 million in investment, leading the number of deals across stages – even though the total amount invested declined compared to late 2024.
Other data shows the UK remains a major hub for tech funding in 2025, with London taking nearly half of all investment activity across stages and regions like the West Midlands and Yorkshire also seeing growth.
These 2025 insights help demonstrate that early-stage investment – including seed funding – remains dynamic and that founders continue to find opportunities despite some volatility in deal size and distribution.
How Does Equity Fundraising Work for Startups?
Quick Definition: Equity fundraising is the process by which startups exchange ownership shares (equity) in their company for capital investment. Unlike loans, there’s no repayment obligation – investors profit when the company grows in value or exits through acquisition or IPO. This is the fundamental mechanism behind seed funding.
Equity fundraising is the cornerstone of startup growth in the UK, governed by the Companies Act 2006 and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) for public offerings and crowdfunding platforms.
1. Step-by-Step Equity Fundraising Process
| Step | What Happens | UK Entities Involved | Typical Documents |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Issue Shares | The company creates new shares to sell to investors | Companies House | Share Certificate, Board Resolution |
| 2. Set Valuation | Determine company worth (pre-money valuation) | Accountants, Advisors | Valuation Report, Financial Projections |
| 3. Pitch Investors | Present the business case to potential investors | Angels, VCs, Platforms | Pitch Deck, Executive Summary |
| 4. Due Diligence | Investors verify claims, financials, and legal standing | Solicitors, Accountants | Data Room, Financial Statements, IP Documents |
| 5. Term Sheet | Negotiate investment terms and conditions | Legal Advisors | Term Sheet, Heads of Terms |
| 6. Shareholder Agreements | Finalise legal agreements and investor rights | Corporate Solicitors | SHA, Articles of Association, Subscription Agreement |
| 7. Filing with Companies House | Register new shares and update company records | Companies House | Form SH01, Updated Register of Members |
2. UK-Specific Regulatory Framework
Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) Oversight:
- Regulates equity crowdfunding platforms such as Crowdcube and Seedrs by Republic, which enable UK SMEs to raise seed funding from retail and accredited investors.
- Ensures investor protection and platform compliance for seed funding transactions
- Requires risk warnings for retail investors participating in seed funding
Companies House Requirements:
- All share issuances from seed funding must be filed within one month
- Annual confirmation statements must reflect updated shareholdings from seed funding
- Public record of company ownership, including seed funding investors, is maintained
Shareholder Rights Under Companies Act 2006:
- Pre-emption rights (existing shareholders’ first refusal on new shares in seed funding rounds)
- Voting rights at general meetings for seed funding investors
- Rights to dividends and company information
- Protection against unfair prejudice
3. Pros & Cons of Equity Funding
Advantages:
- No debt repayments or interest obligations with seed funding
- Access to investor expertise and networks through seed funding
- Tax incentives through SEIS and EIS schemes
- Shared risk with seed funding investors
- Validation of your business model through seed funding
Disadvantages:
- Permanent dilution of ownership from seed funding
- Loss of some control over business decisions after seed funding
- Reporting obligations to seed funding shareholders
- Potential conflicts with seed funding investor expectations
- Longer and more complex seed funding process
4. Practical Example
Scenario: A UK SaaS startup raising £300,000 in seed funding
- Pre-money valuation: £1,000,000 before seed funding
- Post-money valuation: £1,300,000 (pre-money + seed funding investment)
- Equity given: £300,000 ÷ £1,300,000 = 23.1%
- With negotiation buffer: Typically 23-30% depending on seed funding investor terms, SEIS/EIS benefits, and founder leverage
The startup would file Form SH01 with Companies House within one month of completing seed funding, update its share register, and provide new seed funding shareholders with share certificates evidencing their ownership.
How is Seed Investing Different from Other Funding Options?
Seed investing occupies a unique position in the startup funding landscape, characterised by high risk, early traction requirements, and specific investor expectations. Understanding how seed funding differs from other funding types helps founders choose the right capital at the right time.
1. Comprehensive Funding Comparison Table
| Funding Type | Equity Given | Typical Amount (UK) | Investor Type | Risk Level | When It’s Used | Repayment Required | Time to Close |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Seed | 10–20% | £50K–£350K | Founders, Friends & Family, Angels, Accelerators | Very High | Idea validation → MVP | No | 1–3 months |
| Seed | 15–25% | £100K–£2M | Angel investors, Micro-VCs, Seed funds, SEIS/EIS investors | High | MVP → early traction | No | 4–6 months |
| Series A | 15–25% | £2M–£10M | Venture capital firms, Growth investors | Medium–High | Proven model → scaling | No | 6–9 months |
| Series B | 10–20% | £10M–£30M | Growth VCs, Late-stage investors | Medium | Market expansion → profitability | No | 6–12 months |
| Government Grants | 0% | £10K–£200K | Innovate UK, Research Councils | Low | R&D, innovation projects | No | 3–6 months |
| Bank Loans | 0% | £10K–£500K | Banks, alternative lenders | Low–Medium | Revenue-generating stage | Yes (with interest) | 1–3 months |
| Revenue-Based Financing | 0% (revenue share) | £50K–£2M | RBF providers (Uncapped, Karmen) | Medium | Recurring revenue businesses | Yes (% of revenue) | 2–4 weeks |
| Equity Crowdfunding | 5–15% | £50K–£1M | Retail investors via FCA-regulated platforms | Medium–High | Community building + capital | No | 2–3 months |
2. Key Ways Seed Investing Differs
- Focus on Traction Over Revenue
- Seed funding investors expect early product-market fit signals, not profitability
- Key metrics for seed funding: user growth rate (5-20% month-over-month), engagement, retention
- Pre-revenue is acceptable for seed funding if traction metrics are strong
- Equity Expectations
- Seed funding rounds typically involve 15-25% dilution in the UK
- Angel investors often seek 10-15% individually in seed funding
- Seed funds may take 20-25% for lead seed funding investments
- SEIS/EIS tax relief sweetens the deal for seed funding investors (30-50% income tax relief)
- High Uncertainty, High Potential
- Seed funding investors accept that 70-80% of investments may fail
- They seek 10x+ return potential within 5-7 years to compensate for seed funding risk
- Seed funding focuses on founder quality and market size over proven financials
- Less Focus on Current Profitability
- Unlike bank loans or later-stage funding, seed funding investors don’t require positive cash flow
- Seed funding investors invest in future potential based on vision, team, and early validation
- Path to profitability is important for seed funding, but not immediate profitability
- Investor Involvement
- Seed investors often take board observer seats or advisory roles
- More hands-on than later-stage investors
- Provide mentorship, introductions, and strategic guidance
3. UK-Specific Seed Investment Context
Typical UK Seed Round Characteristics:
- Median seed round: £500K- £800K
- Range: £100K- £2M (anything below £100K is typically pre-seed)
- Timeline: 4- 6 months from first pitch to bank transfer
- Investor mix: Often 2- 5 angel investors or 1 lead seed fund plus angels
Common UK Seed Investor Types:
- SEIS/EIS Angels: High-net-worth individuals leveraging tax relief schemes
- Angel Networks: UK Business Angels Association members, syndicates
- Micro-VCs and Seed Funds: Seedcamp, Episode 1 Ventures, Forward Partners
- Accelerators: Techstars London, Entrepreneur First (typically £15K- £150K)
- Corporate VCs: Arm Ventures, Barclays Ventures (sector-specific)
Why Founders Choose Seed Over Alternatives:
- Grants and loans don’t provide enough capital for rapid scaling
- Revenue-based financing requires existing revenue
- Series A requires more traction than most early startups have
- Seed fills the gap between MVP and a scalable business model
Who Provides Seed Investment?
1. Angel Investors
Investment range: £25K- £250K
What they offer: Personal funds, industry expertise, networks
Best for: Early-stage startups with proven founders
Learn more: UK Business Angels Association
Read: Angel Investors vs Venture Capitalists
2. Seed Funds / Micro VCs
Investment range: £100K- £2M
What they offer: Institutional capital, structured support
Examples:
- Seedcamp
- Episode 1 Ventures
- Forward Partners
Read: How to Approach VCs
3. Accelerators & Incubators
Investment range: £15K- £150K
What they offer: Funding plus mentorship, and networks
Examples:
Read: Investors for Startups
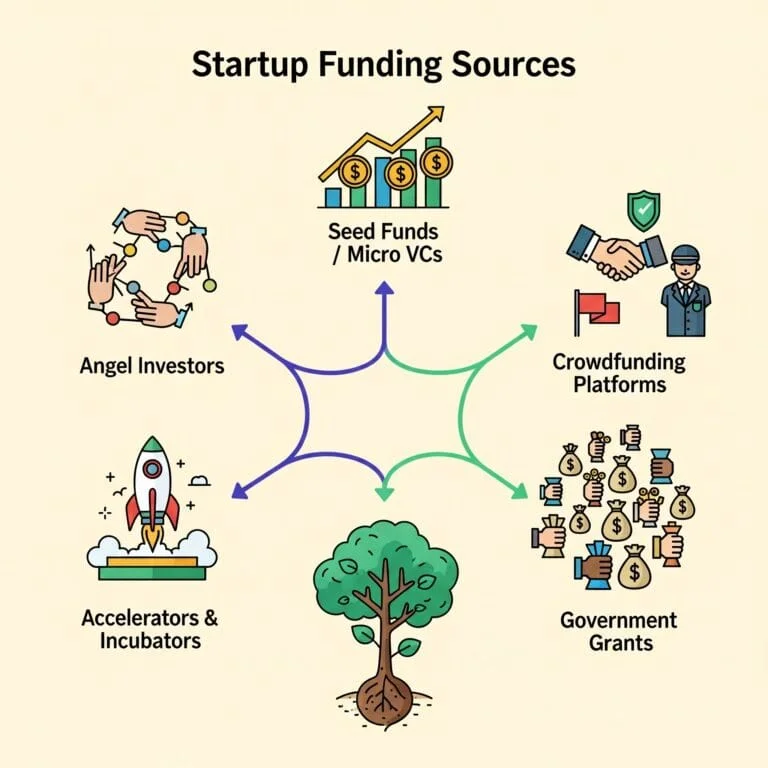
4. Crowdfunding Platforms
Investment range: £50K- £500K
What they offer: Access to retail investors via FCA-regulated platforms
Platforms:
Read: Crowdfunding for Startups
5. Government Grants
Investment range: £10K- £200K
What they offer: Non-dilutive funding with tax benefits
Programs:
Read: Small Business Funding Options
6. Friends & Family
Investment range: £5K- £50K
What they offer: Initial capital from trusted networks
Best for: Very early-stage proof of concept
Read: Raising Startup Funds from Friends & Family – Dos & Don’ts
How to Align with Investor Expectations
What Seed Investors Want
Market Size and Opportunity
Expectation: Addressable market of £1B+ with clear growth trajectory
How to align: Present TAM, SAM, and SOM with validation data
Strong Founding Team
Expectation: Complementary skills and full-time commitment
How to align: Highlight relevant experience and clear role definitions
Traction and Validation
Expectation: Evidence of product-market fit and customer demand
How to align: Provide user metrics, testimonials, and retention data
Scalable Business Model
Expectation: Clear path to profitability and revenue growth
How to align: Present unit economics and 3-year projections
Competitive Advantage
Expectation: Defensible moat and differentiation
How to align: Show unique value proposition and barriers to entry
Exit Potential
Expectation: 10x+ return potential within 5-7 years
How to align: Research comparable exits and potential acquirers

Is Your Startup Ready for Seed Funding?
Essential Prerequisites Checklist
- Clear problem-solution fit with validated customer pain points
- Basic MVP (Minimum Viable Product) or working prototype
- Market validation (waitlist signups, early users, customer interviews)
- Committed founding team with complementary skills
- Initial business plan with a clear funding allocation strategy
- Legal structure (UK Limited Company for equity investment)
Advanced Readiness Indicators
- Early traction metrics showing user engagement
- Customer feedback loops and product iteration cycles
- Competitive analysis and market positioning
- Financial projections with realistic assumptions
- Team expansion plan for key hires
If you’re missing several of these, focus on building your MVP and gaining initial traction before approaching investors.

From Seed to Series A – Milestones and Typical KPIs
Understanding the funding progression from seed to Series A and beyond is critical for planning your startup’s growth trajectory. Each stage has distinct milestones, investor expectations, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
1. Funding Progression Timeline
Pre-Seed → Seed → Series A → Series B → Series C+
(Idea) (MVP) (Scale) (Growth) (Expansion)
2. Stage-by-Stage Breakdown Table
| Stage | Milestones | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Typical UK Raise | Investor Expectations | Equity Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Seed |
• Idea validation • Team formation • Market research • Basic prototype |
• Customer interviews conducted • Problem–solution fit validated • Founding team committed full-time |
£50K–£350K |
• Clear problem worth solving • Passionate, capable founders • Large addressable market |
10–20% |
| Seed |
• MVP launched • First paying customers • Product–market fit signals • Initial team hires • Go-to-market strategy |
• 5–20% MoM growth • £10K–£100K ARR/MRR • 100–1,000 active users • 20–40% retention (30 days) • Basic unit economics |
£100K–£2M |
• Clear problem–solution fit • Early traction and growth • Scalable business model • Strong founding team |
15–25% |
| Series A |
• Proven business model • Consistent revenue growth • Expanded team (10–30 people) |
• £1M–£3M ARR • 15–30% MoM growth • CAC < 12 months payback • 60%+ gross margin • LTV:CAC ratio 3:1+ |
£2M–£10M |
• Proven product–market fit • Scalable acquisition channels • Clear path to profitability • Strong unit economics |
15–25% |
| Series B |
• Market leadership position • Multi-channel distribution • Team 50–100+ people • International expansion |
• £5M–£15M ARR • 10–20% MoM growth • Magic number > 0.75 • 70%+ gross margin • Net retention > 100% |
£10M–£30M |
• Proven growth engine • Market expansion capability • Path to profitability clear • Strong competitive moat |
10–20% |
| Series C+ |
• Market dominance • Multiple product lines • M&A activity • IPO preparation |
• £15M+ ARR • Rule of 40 achieved • Positive cash flow • 80%+ gross margin • Efficient growth at scale |
£30M+ |
• Clear path to exit / IPO • Profitable or near-profitable • Market leader position • Sustainable competitive advantage |
5–15% |
3. KPIs Needed to Move from Seed → Series A
Making the leap from seed to Series A requires demonstrating proven, repeatable growth. Here are the critical metrics investors look for:
Revenue & Growth Metrics:
- £1M+ Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) or clear path to it within 6 months
- 15- 30% month-over-month growth sustained for 6+ months
- Revenue retention >90% (monthly) or >100% net retention (with upsells)
Customer Acquisition:
- CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost) payback < 12 months
- Multiple validated acquisition channels (not dependent on one source)
- Sales cycle understood and optimised
- Repeatable sales process in place
Product & Engagement:
- Product-market fit clearly demonstrated (strong NPS, low churn)
- Daily/Weekly Active Users are growing consistently
- Feature adoption rates are increasing
- Customer testimonials and case studies
Team & Operations:
- 10- 30 employees with a clear organisational structure
- Key leadership roles filled (CTO, Head of Sales/Marketing)
- Defined company culture and values
- Operational processes documented
Financial Health:
- LTV: CAC ratio of 3:1 or better
- Gross margins >60% (SaaS) or >40% (marketplace/hardware)
- 12- 18 months of runway remaining
- Clear understanding of unit economics
4. Examples of Traction Signals by Stage
Seed Stage Traction:
- “We’ve grown from 0 to 500 active users in 3 months”
- “Our waitlist has 2,000 signups with a 30% activation rate”
- “We’re processing £10K MRR with 25% month-over-month growth”
- “Five paying customers with an average contract value of £5K/year”
Series A Traction:
- “We’ve reached £1.5M ARR, growing at 20% monthly”
- “Our CAC is £800 with LTV of £3,200 (4:1 ratio)”
- “We have 50+ enterprise customers with 95% retention”
- “Three validated acquisition channels each driving 30%+ of growth”
5. Team Expansion Expectations
| Stage | Typical Team Size | Key Roles to Add | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Seed | 1–3 | Co-founders only | Building MVP, validating the idea |
| Seed | 3–10 | Engineers, first sales/marketing hire | Product development, initial traction |
| Series A | 10–30 |
Head of Sales, Marketing Lead, Product Manager, Senior Engineers |
Scaling go-to-market, building sales team |
| Series B | 30–100 |
VPs of Sales / Marketing / Product, Finance Lead, HR Manager |
Building department teams, operational infrastructure |
6. Investor Psychology Across Stages
Seed Stage: Belief in Founders
- Investors back the team more than the traction
- Looking for coachability, resilience, and domain expertise
- Willing to accept higher uncertainty with strong founding teams
- “Can these founders execute and pivot as needed?”
Series A: Belief in Traction
- Proof of product-market fit becomes paramount
- Data-driven decision making expected
- Repeatable growth demonstrated
- “Is there a scalable business model here?”
Series B: Belief in Scalability
- Focus shifts to growth efficiency and market capture
- Unit economics must be strong
- Proven ability to scale operations
- “Can this company become a category leader?”
Example Progression: UK FinTech Startup
Pre-Seed (2023): £100K raised from angels
- Founders with 10+ years of banking experience
- Validated problem through 50 customer interviews
- Built a clickable prototype
Seed (2024): £750K raised from seed fund + EIS investors
- Launched MVP with 500 beta users
- £15K MRR growing 20% monthly
- 2 co-founders + 3 engineers
Series A Target (2026): Aiming for £3M
- Current metrics: £1.2M ARR, 25% MoM growth
- 1,200 paying customers, 92% retention
- Team of 15, including Head of Sales
- CAC payback: 9 months, LTV: CAC ratio 4:1
RSVR Tech: Building the Technical Foundation for Seed-Stage Startups
RSVR Tech partners with UK startups at the seed stage to design, build, and validate robust MVPs and define clear technical strategies that support long-term growth. We work closely with founders to turn early ideas into scalable products that are ready for real users, real feedback, and real traction.
Our experience spans multiple sectors, including FinTech, HealthTech, and CleanTech, where technical quality, security, and scalability are critical from day one.
How RSVR Supports Seed-Stage Startups
- MVP Design & Development: We build lean, market-ready MVPs that prioritise core functionality, speed to market, and future scalability.
- Technical Strategy & Architecture: Clear technology roadmaps, architecture decisions, and stack selection aligned with your business goals and growth plans.
- Product Validation Support: Helping founders test assumptions, iterate based on user feedback, and refine products before scaling.
- Engineering Best Practices: Clean code, scalable architecture, and security-conscious development to avoid technical debt early on.
- Founder-Focused Collaboration: We act as a long-term technical partner, working alongside founders to evolve the product as the business grows.
RSVR Tech focuses on building strong technical foundations – so when founders move into fundraising or scaling, their product is ready to support it.
Contact us to discuss how we can help you build, validate, and scale your MVP with confidence.
UK Seed Funding Success Stories
To understand what a successful UK seed round looks like in practice, it helps to examine real-world examples. While every startup’s journey is different, these cases highlight common patterns in traction, investor fit, and outcomes at the seed stage.
1. Monzo (FinTech)
- Seed Stage Focus: Early product validation and customer adoption
- Seed Funding: Raised a multi-million-pound seed round from a mix of UK angel investors and early-stage venture funds
- Key Outcome: Rapid user growth and strong product-market fit enabled Monzo to progress quickly into Series A and beyond
- Lesson for Founders: Clear consumer pain points, strong UX, and early traction can attract high-quality seed investors even in regulated sectors
2. Huel (Consumer / DTC)
- Seed Stage Focus: Product differentiation and brand positioning
- Seed Funding: Secured seed capital from private investors to scale production and marketing
- Key Outcome: Built a loyal customer base early, supporting sustainable growth without immediate heavy VC dependence
- Lesson for Founders: Seed funding doesn’t always mean hypergrowth – clarity of brand, unit economics, and demand can be equally compelling
3. Cazoo (Marketplace / Automotive)
- Seed Stage Focus: Building a scalable technology platform and operational model
- Seed Funding: Raised seed capital from early-stage investors before accelerating into larger venture rounds
- Key Outcome: Used seed funding to validate a complex business model before aggressive expansion
- Lesson for Founders: Seed investors back strong execution plans when paired with ambitious but credible market opportunities
Key Takeaways from Successful UK Seed Rounds
- Seed funding is primarily about belief in the team and early evidence of demand
- Clear articulation of the problem and solution matters more than polished scale metrics
- Investors look for momentum – whether that’s users, revenue, pilots, or engagement
- Strong technical foundations and execution capability significantly improve fundraising readiness
These examples show that while funding amounts and timelines vary, successful seed rounds consistently combine founder credibility, early traction, and a clear path forward.
How Much Can You Raise in Seed Funding?
1. Seed Funding Ranges
Typical UK Seed Rounds:
- Lower end: £100K- £500K (first-time founders, B2C products)
- Mid-range: £500K- £1M (experienced founders, proven traction)
- Upper end: £1M- £2M (serial entrepreneurs, competitive markets)
- Outliers: £2M+ (exceptional teams, hot sectors like AI/FinTech)
2. Factors Affecting Funding Amount
- Founder Experience
- First-time founders: £100K- £500K
- Second-time founders: £500K- £1.5M
- Serial successful founders: £1M- £3M+
- Sector and Market
- Software/SaaS: £300K- £1M
- FinTech/HealthTech (regulated): £500K- £2M
- Hardware/DeepTech: £800K- £2M+
- CleanTech: £500K- £1.5M
- Traction Level
- Pre-revenue MVP: £100K- £300K
- Early revenue (£10K- £50K MRR): £300K- £800K
- Strong traction (£50K+ MRR): £800K- £2M
3. Key Takeaway
Seed funding ranges: £100K- £2M for most UK startups, with the median around £500K- £800K.
These ranges are based on aggregated data from UK-focused venture intelligence platforms such as Beauhurst, Dealroom, and PitchBook, alongside publicly disclosed SEIS/EIS-backed seed rounds and accelerator reports. Actual amounts vary by sector, founder profile, and market conditions.
Alternative Funding Mechanisms
1. Revenue-Based Financing (RBF)
How it works: Investors provide capital for a percentage of future revenue
Best for: SaaS companies with predictable recurring revenue
UK providers: Uncapped, Karmen
Typical Terms:
- Repayment: 2- 8% of monthly revenue until 1.3- 2.5x repaid
- No equity dilution
- Faster than equity raises (2- 4 weeks)
2. Convertible Instruments
Simple Agreement for Future Equity (SAFE):
- Faster to close than priced rounds
- Converts to equity in future funding round
- Popular with accelerators and angel investors
- Common terms: 10- 20% discount, £3M- £8M valuation cap
Convertible Loans:
- Debt that converts to equity
- Include interest rates (8- 12% typical) and conversion discounts
- Common in UK seed funding
- Mature in 12- 36 months
3. Equity Crowdfunding
Benefits:
- Access to retail investors
- Marketing and brand awareness benefits
- Community building
- Typical raise: £50K- £500K
Regulation: FCA-regulated with investor protections under the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000
4. Government Funding
Innovate UK Grants:
- Up to £200K for innovative projects
- Non-dilutive funding
- Requires matched funding in some schemes
- Apply here
SEIS Tax Relief:
- Up to £150K annually with 50% income tax relief for investors
- The company must be less than 3 years old
- Gross assets under £350K
- Learn more
EIS Tax Relief:
- Up to £5M annually (£12M lifetime)
- 30% income tax relief for investors
- Learn more
Seed vs Pre-Seed vs Series A Funding
| Stage | Typical Funding (UK) | Investor Types | Primary Focus | Equity Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre‑Seed | £50K–£350K | Founders & Friends/Family, Angel investors, Accelerators | Idea validation, MVP | 10–20% |
| Seed | £500K–£2M | Angels, Micro‑VCs, Seed funds | MVP + early traction, team building | ~20% (range 15–25%) |
| Series A | £2M–£10M | VC firms, Growth investors | Scaling and go‑to‑market | ~20% (range 15–25%) |
Key Differences Explained
Pre-Seed Focus:
- Proving concept viability
- Building an initial prototype
- Conducting market research
- Assembling the founding team
Seed Focus:
- Achieving product-market fit
- Building an initial customer base
- Hiring key team members
- Establishing a business model
Series A Focus:
- Scaling a proven business model
- Expanding market reach
- Building sales and marketing teams
- Preparing for rapid growth
Key Differences Explained
- Seed funding ranges: £100K–£2M for most UK startups
- Equity expectations: 15-25% dilution is standard
- Timeline: Allow 4-6 months for the fundraising process
- Readiness: Have an MVP, traction, and a clear business model
- Alternative options: Consider RBF, convertible instruments, and government grants
Final Thoughts on Securing Seed Investment
Seed funding isn’t just about raising money – it’s about finding the right partners to support your startup journey. The UK startup ecosystem continues to evolve, with new funding mechanisms and investor types emerging regularly.
Focus on building a business that creates real value for customers, maintain strong relationships with potential investors, and remember that fundraising is a means to an end, not the end itself. Use seed funding strategically to achieve key milestones that will position your startup for future growth and success.
Ready to take the next step? Contact RSVR Tech today to discuss your seed funding strategy and how we can support your startup’s growth journey.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What counts as seed funding in the UK?
Seed funding is an early-stage investment (typically £100K- £2M) in exchange for equity, used to develop products and prove market fit before significant revenue generation.
How much equity do startups give up in seed rounds?
How long does it take to close a seed funding round?
4-6 months from initial outreach to funding completion, including 2-3 months for preparation and 2-3 months for active fundraising.
Can you get seed funding without revenue?
Yes, many seed-stage companies are pre-revenue. Focus on demonstrating traction through user metrics, partnerships, or market validation rather than revenue.
What documents do I need for seed funding?
- Executive summary (2 pages)
- Pitch deck (10-15 slides)
- Financial projections (3 years)
- Product demo or prototype
- Legal documentation (articles of incorporation, cap table)
What's the difference between angel investors and VCs?
Angel investors invest personal funds and typically write smaller checks (£25K- £100K). VCs manage institutional funds and write larger checks (£100K- £2M+).
Should I use a lawyer for seed funding?
Yes, especially for equity raises. Legal costs typically range from £5K- £15K, but protect against future complications.
How much can first-time founders raise?
First-time founders typically raise £100K- £500K in seed funding, while experienced founders can raise £500K- £2M or more.
What are SEIS and EIS?
SEIS (Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme) and EIS (Enterprise Investment Scheme) are UK government tax relief programs that incentivise investment in early-stage companies by offering income tax relief to investors (50% for SEIS, 30% for EIS).
Do I need to register my seed round with Companies House?
Yes, all share issuances must be filed with Companies House using Form SH01 within one month of the transaction.








